Applying MapCalc Map Analysis Software
Travel-Time and Customer Access: A market analyst needs to construct an
“underlay” for a client’s MapInfo database that shows the travel-time from
<click here>
for a printer friendly version (.pdf)
Base Maps. Standard
MapInfo layers of streets, water and stores (
 Composite Display. Standard
MapInfo layers of streets, water and stores (
Composite Display. Standard
MapInfo layers of streets, water and stores (
Step 1. The
base maps in MapInfo are
transferred to MapCalc for analysis.
 Pseudo
Grid. A “pseudo grid” is
constructed in MapInfo. Each grid cell
is treated as a polygon forming 160 columns by 130 rows = 20,800 cells that
comprise the analysis window. The insert
in the lower left portion of the figure is an enlarged portion clearly showing
the pseudo grid cells.
Pseudo
Grid. A “pseudo grid” is
constructed in MapInfo. Each grid cell
is treated as a polygon forming 160 columns by 130 rows = 20,800 cells that
comprise the analysis window. The insert
in the lower left portion of the figure is an enlarged portion clearly showing
the pseudo grid cells.
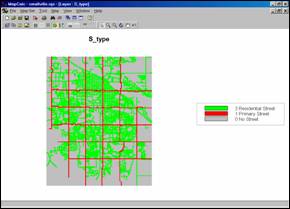 S_type Map. Any MapInfo data layer (points, lines,
polygons) can be “burned” into a similarly configured MapCalc analysis
grid. For example, a grid-map of the MapInfo
“streets” layer is imported into MapCalc.
Each cell identifies whether a street is present with a separate value
for the type of street (1=
S_type Map. Any MapInfo data layer (points, lines,
polygons) can be “burned” into a similarly configured MapCalc analysis
grid. For example, a grid-map of the MapInfo
“streets” layer is imported into MapCalc.
Each cell identifies whether a street is present with a separate value
for the type of street (1=
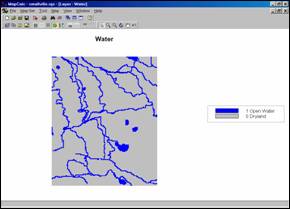 Water Map. In a similar fashion, a grid-map of the water
features is imported into MapCalc from MapInfo.
The map identifies the presence of surface water (1= Open Water…blue).
Water Map. In a similar fashion, a grid-map of the water
features is imported into MapCalc from MapInfo.
The map identifies the presence of surface water (1= Open Water…blue).
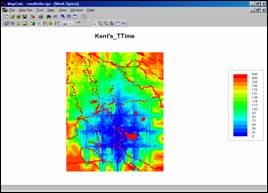
Step 2. Using
the proximity tool in MapCalc a travel-time distance is assigned to each of the
20,800 cells within the analysis window (see the “Proximity Demo” for
discussion of how proximity surfaces are generated).
The 3-D surface on
the right shows the increasing travel-time as a “bowl” with the lowest point
being at the store (0 away from the store) and increasing time to all other
locations. Note the big spikes
indicating rapidly increasing travel-time for the non-road areas at the corners
of the map. The southwest corner is the
farthest away (545 units * 6 sec per unit= 3270 sec / 60 sec per min= 54.5 min
by walking then by car along the fastest route).
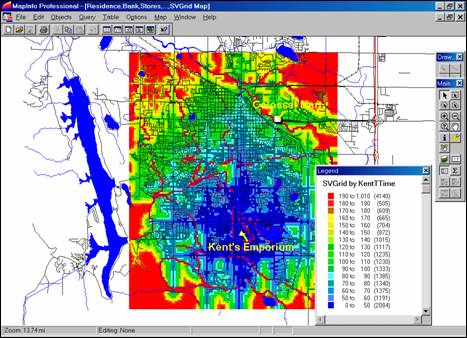
Step 3. The
travel-time map generated in MapCalc is imported into MapInfo by appending the
cell values to the pseudo grid table.
 The farthest away location on a street is
nearly 20 minutes (199 units * 6 sec per unit= 1194 sec / 60 sec per min= 19.9
min). Potential customers on this street
need strong motivation to visit the store.
The farthest away location on a street is
nearly 20 minutes (199 units * 6 sec per unit= 1194 sec / 60 sec per min= 19.9
min). Potential customers on this street
need strong motivation to visit the store.
Summary.
Travel-time analysis is an important part of
Note: A similar exchange of information between
MapCalc and ArcView/ArcInfo users can be
made. See the Determining Proximity
application for discussion of the procedures used in calculating effective
proximity.